As the B2B market for clothing manufacturing grows, brands are often faced with the decision of choosing between OEM and ODM manufacturers. Understanding the differences between these two types of manufacturers can significantly impact product development, brand identity, and the overall business strategy. In this article, we’ll break down the concepts of OEM and ODM, helping brands make informed choices.
What Are OEM and ODM?
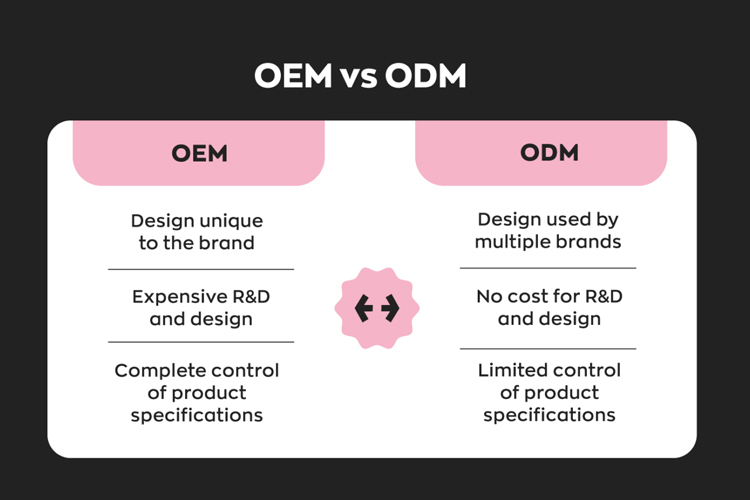
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to manufacturers that provide production services based on a brand’s unique design or specifications. In other words, they don’t own the design; they simply bring the brand’s vision to life by manufacturing products that meet the given requirements.
ODM (Original Design Manufacturer)
On the other hand, ODM manufacturers offer both design and manufacturing services. They create products that can either be branded and marketed directly by clients or customized according to specific brand preferences. ODM manufacturers play a larger role in product development, making them ideal for brands looking for a more comprehensive service solution.
Scope of Services
Differences in OEM and ODM Services
The scope of services varies significantly between OEM and ODM, each catering to different brand needs.
OEM Services
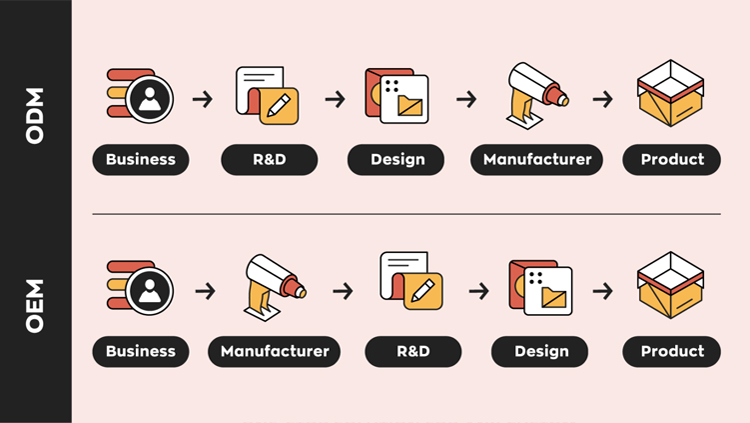
OEM focuses on production. Clients typically provide detailed designs and specifications, and the manufacturer is responsible for production only. This model is suited to brands with a complete design in place, looking to leverage efficient manufacturing capabilities.ODM Services
ODM offers a full suite of services, from concept design to production. Brands can either use the manufacturer’s pre-existing designs or work together to create custom products. This model provides flexibility and is especially beneficial for startups or companies looking to launch new products without handling the initial design phase.
Relationship with Clients
Different Client Relationships with OEM and ODM
Each model fosters a unique client relationship and partnership approach.
OEM: Production-Focused Partnerships
OEM works well for established brands with fully-developed designs. These clients prioritize production efficiency and scaling capabilities over design input, as they already possess a strong brand identity and design language.ODM: Collaborative Partnerships
ODM manufacturers often work with emerging brands or companies seeking product innovation. These partnerships emphasize collaboration and creative input, as manufacturers assist clients in creating new designs. Brands often rely on the manufacturer’s expertise to expedite product development and achieve unique market positioning.
Brand Control
Impact on Brand Control in OEM and ODM Models
Both OEM and ODM models affect the level of control brands have over their products and brand identity.
OEM for Higher Brand Control
Brands retain a high level of control in the OEM model. Since the design originates from the client, they can ensure that the product aligns with their brand image, values, and target audience.ODM and Design Flexibility
While ODM provides comprehensive design services, brands may experience a reduction in control over design elements. However, the trade-off is a faster time-to-market, as the manufacturer’s design expertise and market insight streamline the product development process.
Cost and Risk Factors
Comparing Cost Structures and Risks in OEM and ODM
Costs and risks also differ between OEM and ODM models, which is essential to consider for sustainable business growth.
OEM: Cost Efficiency with Higher Client Responsibility
OEM manufacturing is often cost-effective for large-scale production, as it eliminates the need for design and development resources from the manufacturer. However, the client assumes all design-related risks, from market fit to regulatory compliance.ODM: Upfront Investment with Reduced Market Risks
ODM requires a higher initial investment for design and development. Nevertheless, it can mitigate market risks, as the manufacturer’s insights and R&D capabilities support product design, potentially increasing market alignment and appeal.
Suitable Scenarios for OEM and ODM
When to Choose OEM or ODM?
Choosing between OEM and ODM depends on the brand’s goals, resources, and market strategy.
OEM for Established Brands with Unique Designs
Brands with strong design departments and a clear vision usually opt for OEM to maintain control over product aesthetics and branding.ODM for Startups and Companies Entering New Markets
ODM is beneficial for startups or brands venturing into new product categories. The collaborative approach allows them to leverage the manufacturer’s design capabilities, reducing development time and achieving faster market entry.
Example:
A luxury brand with proprietary designs may choose OEM to ensure quality manufacturing that strictly follows its design blueprint. A new sportswear brand, however, might find ODM advantageous, as it allows them to launch products quickly by utilizing the manufacturer’s existing design templates and technical know-how.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In summary, both OEM and ODM clothing manufacturing models offer unique advantages:
- OEM allows brands to maintain control over designs, making it ideal for established companies with proprietary designs looking for production-only services.
- ODM provides a comprehensive service, from design to production, making it an excellent choice for brands seeking innovative products and faster time-to-market.
When deciding between OEM and ODM, consider your brand’s current needs, market goals, and available resources. As a leading clothing manufacturer, YiMeng Garments offers both OEM and ODM solutions. Contact us today to discuss which model best suits your brand and production needs.







