What is a Clothing Pattern? An In-depth Guide for B2B Buyers
In the garment manufacturing industry, clothing patterns are essential for producing quality products that meet modern fashion standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding clothing patterns can provide valuable insights into the production process, aiding in selecting the right manufacturers and assessing the quality of the end products. This article dives into the concept, types, processes, and innovations in clothing pattern making, aimed at helping B2B clients make informed decisions.
What is a Clothing Pattern?
Definition and Basic Concept
A clothing pattern, also known as a garment pattern or fashion pattern, is a template used to cut the various fabric pieces needed to construct a garment. Patterns are typically created by skilled pattern makers who work from the designer’s sketch or a sample garment, transforming the concept into a two-dimensional paper or digital layout that guides the cutting and assembly process.
Clothing patterns play a pivotal role in apparel production by ensuring consistency in size, shape, and style. In mass production, these patterns are vital for producing large quantities of garments that retain the same fit and design details.
Types of Clothing Patterns
Basic Patterns
Basic patterns, also called slopers or blocks, are foundational templates for standard garment shapes, like a simple T-shirt, dress, or pair of pants. These patterns do not contain specific design elements and are often used as starting points for creating more complex, customized patterns.
Design Patterns
Design patterns are modified from the basic patterns to include specific fashion details like collars, pleats, or tailored fits. These patterns represent the designer’s unique vision and define the garment’s final aesthetic, adding a layer of creativity to the production process.
Sample Patterns
Sample patterns are used to create prototype garments, or “samples,” which are typically tested for fit, comfort, and style before mass production. These patterns are often adjusted multiple times to meet the designer’s or client’s specific standards.
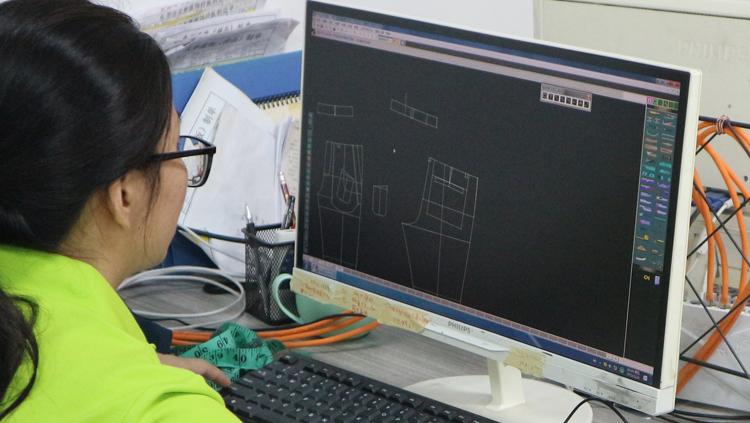

Steps to Create a Clothing Pattern
Step 1: Initial Sketch and Design Specifications
The process begins with a detailed sketch or design concept provided by the designer or brand. This sketch includes critical information, such as dimensions, fabric types, and stylistic elements.
Step 2: Selecting and Drafting the Basic Pattern
Using the initial sketch as a reference, pattern makers select or create a basic pattern. This foundational template will later be modified to suit the design’s requirements.
Step 3: Pattern Modification and Grading
The pattern is modified to match the unique elements of the design. Grading involves adjusting the pattern for different sizes, which is essential for producing garments in various dimensions without altering the core design.
Step 4: Pattern Testing and Adjustment
A prototype is made from the sample pattern, which is then tested for fit and comfort. Necessary adjustments are made, and the pattern may undergo several revisions until it meets the desired specifications.
Tools and Software Used in Pattern Making
Traditional tools include rulers, scissors, and measuring tapes, which are still commonly used. However, many manufacturers also rely on advanced CAD software like Gerber or Optitex, which allows pattern makers to create, modify, and store patterns digitally for improved efficiency and accuracy.

Adjusting and Correcting Patterns
Adjustments for Fit and Function
During the creation and testing phases, adjustments may be necessary to ensure that the garment fits correctly. Common adjustments include resizing for different body types or modifying the design for added comfort and durability.
Common Pattern Issues and Solutions
- Misalignment of Seams: Seams that do not align can affect the garment’s appearance and fit. Pattern makers can correct this by adjusting seam allowances or tweaking the design lines.
- Improper Fit: If a sample garment doesn’t fit as expected, adjustments to the pattern dimensions can be made to ensure a comfortable fit.
The Role of Patterns in Garment Production
Ensuring Consistency and Fit
Patterns are instrumental in maintaining consistent sizing, helping manufacturers produce garments that meet quality standards. This reduces waste and improves production efficiency, as fabric is precisely cut according to the pattern.
Reducing Waste and Optimizing Production
With precise pattern layouts, manufacturers can minimize fabric waste, which is a cost-effective and environmentally sustainable approach. Patterns also help speed up the production process, as they provide a clear guide for cutting and assembling each garment.
Meeting Market Demands
As fashion trends evolve, patterns allow manufacturers to quickly adapt to new styles without reinventing the design from scratch. This flexibility is crucial for B2B clients who need to respond swiftly to market demands.
Modern Technology and Pattern Making
Impact of 3D Printing and Automation
Innovations like 3D printing enable designers to create three-dimensional garment prototypes before making patterns, which speeds up the design process. Automation, including digital pattern grading and cutting, reduces human error and increases production speed, which is essential for large-scale orders.
Virtual Fitting Technology
Virtual fitting technology allows designers and manufacturers to simulate how a garment will fit before it’s physically produced. This can reduce the need for multiple prototypes, saving time and resources, and providing a clear preview for B2B clients.
Case Studies and Insights from the Industry
Successful Pattern Making Case Studies
Several companies have successfully implemented digital pattern-making tools and automation, achieving high levels of efficiency and accuracy. For instance, a sportswear company used CAD software to speed up the pattern creation process, reducing production time by nearly 30% and resulting in fewer returns due to sizing issues.
Tips for B2B Buyers
For B2B buyers, selecting manufacturers who use advanced pattern-making technologies can ensure higher quality, consistency, and faster production times. Buyers should look for manufacturers who understand the importance of pattern accuracy and have experience in managing large orders with diverse size requirements.
Conclusion and Future Trends in Pattern Making
Clothing patterns form the backbone of garment design and production. With the integration of advanced technology, pattern-making processes continue to evolve, offering enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability. As the industry moves towards more digitalized and automated production systems, B2B buyers can expect even greater precision and flexibility in the near future.







